What is a distributed system?
Published on November 7, 2025
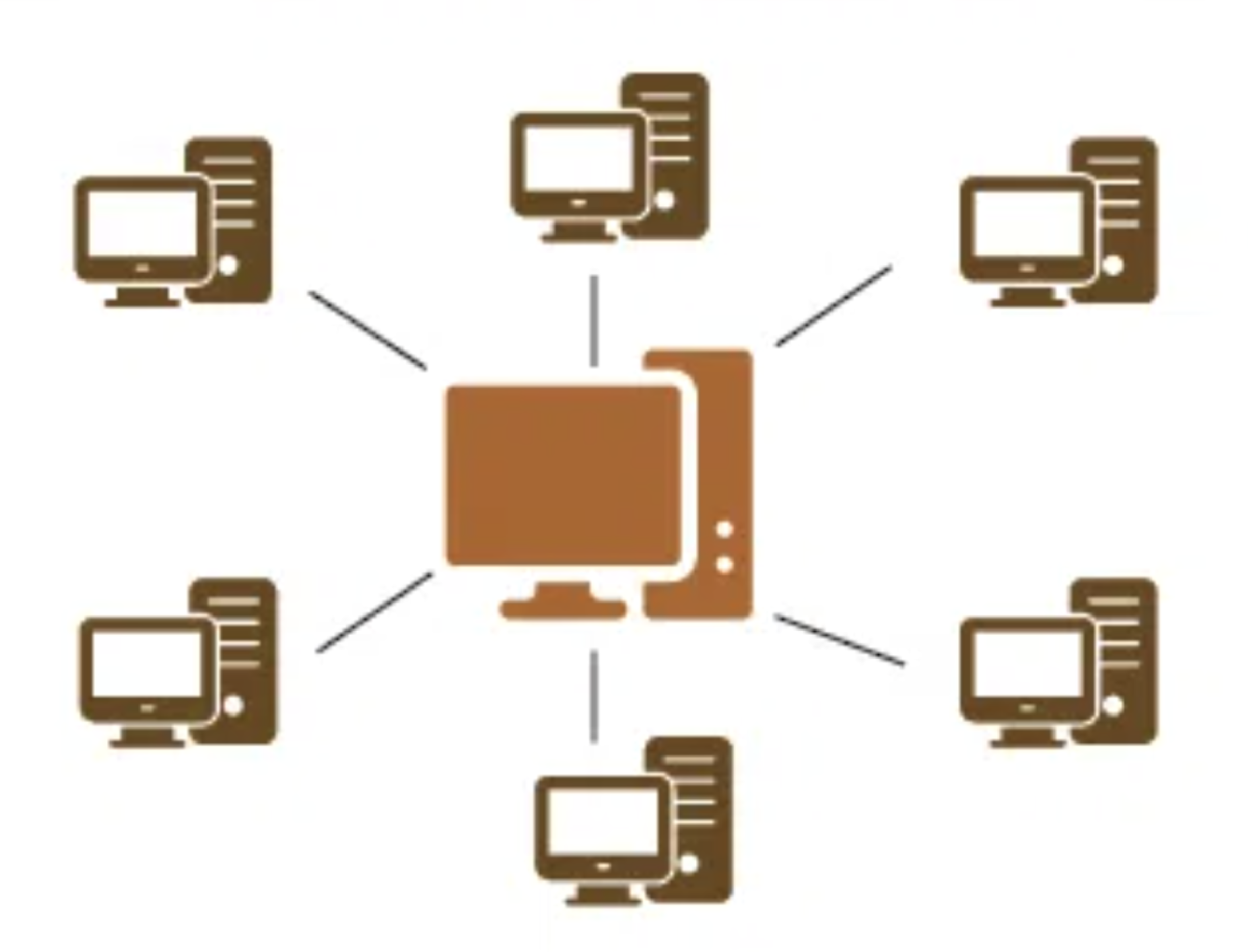
What is a Distributed System?
A distributed system is a collection of independent computers that work together to solve a problem or perform a task. In a distributed system, each computer (also called a node or a server) operates independently, but can communicate and coordinate with other nodes in the system.
Distributed systems are used in a variety of applications where scalability, fault tolerance, and geographical distribution are critical. They have become increasingly popular in recent years due to the explosion of data and the need to process large amounts of data quickly and efficiently.
Advantages of Distributed Systems
There are several advantages to using a distributed system:
-
Scalability: Distributed systems can handle a large amount of data or a large number of users by distributing the load across multiple nodes. As the load increases, additional nodes can be added to the system to handle the increased demand.
-
Fault Tolerance: Distributed systems can provide redundancy and failover mechanisms to ensure the system continues to operate even if individual nodes fail. If a node fails, the system can automatically switch to a backup node without any interruption to the service.
-
Geographical Distribution: Distributed systems can be geographically distributed to reduce network latency and improve performance. By placing nodes closer to users or resources, the system can reduce the time it takes to transmit data between nodes.
Disadvantages of Distributed Systems
There are also several disadvantages to using a distributed system:
-
Complexity: Distributed systems are more complex than centralized systems because they require coordination and communication between multiple nodes. This complexity can make it more difficult to design, develop, and maintain the system.
-
Security: Distributed systems are more vulnerable to security threats because they have more points of entry for attackers. It can be more difficult to ensure that all nodes in the system are secure and that data is protected.
-
Cost: Distributed systems can be more expensive to develop and maintain than centralized systems because they require more hardware and software resources.
Core Concepts of Distributed Systems
To understand distributed systems, it is important to understand some of the core concepts:
-
Communication: Nodes in a distributed system communicate with each other to exchange data and coordinate their actions. This communication can be synchronous or asynchronous, and can use various protocols and technologies.
-
Consistency: In a distributed system, it is important to ensure that all nodes have a consistent view of the system. This can be achieved through various consensus algorithms and techniques, such as leader election, replication, and synchronization.
-
Partitioning: Distributed systems often use partitioning to divide data and processing across multiple nodes. This can improve scalability and performance by allowing each node to operate independently on a smaller subset of the data.
-
Fault Tolerance: Distributed systems can use various mechanisms to provide fault tolerance, such as replication, redundancy, and failover. These mechanisms ensure that the system continues to operate even if individual nodes fail.
Examples of Distributed Systems
Here are some real-life examples of distributed systems:
-
Social Media Platforms: Social media platforms like Facebook and Twitter are examples of distributed systems. These platforms use a large number of servers distributed across data centers around the world to handle the large number of users and data they generate.
-
E-commerce Websites: E-commerce websites like Amazon and eBay use distributed systems to handle the large number of users and transactions they process. These systems use distributed databases, caching layers, and load balancers to ensure high availability and scalability.
-
Cloud Computing: Cloud computing platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure are examples of distributed systems. These platforms use a large number of servers distributed across data centers to provide services like storage, computing, and networking to customers